Detailed Description
The finite field part of the kernel provides finite field arithmetic and basic operations with vectors and matrices over finite fields.
The kernel cannot operate simultaneously with different finite fields, because there is a global row size and a global field order which must be maintained by the higher layers.
There are two finite field modules available: one for small fields (up to 256) and one for larger fields (up to 216). The finite field module is selected at compile time.
Basic data types
The kernel defines two basic data types:
- FEL
- represents a single field element
- PTR
- is a pointer to a row vector. PTR may be defined as
*FEL, but this is not mandatory.
The kernel also defines two constants: FF_ZERO is the zero element of the current field, and FF_ONE is unit element of the current field. Depending on which kernel you are using, FF_ZERO and FF_ONE need not be constants. They may be defined as variables or even function calls.
Internal data representation
- 'Small' Kernel (q≤256)
- In the "small" kernel, field elements of GF(q) are represented by the numbers 0,1,...,q-1. The field is defined by its Conway polynomial p(x), a polynomial of degree n over ℤp[x], where q=pn. Thus, we have a one-to-one correspondence of field elements a∈GF(q) and polynomials fa(x)∈ ℤp[x] of
degree less than n. By treating ℤp as a subset of ℤ — actually, on the computer, elements of ℤp are represented by integers — this is also a polynomial over *ℤ. Now, calculate f_a(p) giving the number of the field element a. It follows that the elements of the prime field are represented by 0,1,...p-1. The number 0 represents the zero element, and 1 represents the unit element.
- 'Big' Kernel (q≤65536)
- The big version stores field elements in 16-bit integers, i.e., each field element occupies two bytes. Non-zero elements are stored as their logarithms with respect to a fixed generator. In particular, the unit element is represented by the integer 0. The zero element is represented by the special value 0xFFFF.
As a consequence of the different representations of field elements in the small and big version, there are some rules which should be respected by all programs:
- Never assign numbers to variables of type FEL or pass numbers to functions expecting an argument of type FEL.
- Never perform integer arithmetic on variables of type FEL.
- Never printf() or scanf() variables of type FEL.
- Never use the literals 0 or 1 where the zero and unit element of the field is intended. Instead you should use the FF_ZERO and FF_ONE constants define in |meataxe.h|.
- Do not cast an integer to FEL or vice versa. Use FfFromInt() and FfToInt() instead.
Converting between finite field elements and integers
The MeatAxe defines a standard numbering of field elements, i.e., a bijection between GF(q) and the set {0,1,..,q-1}. For prime fields, the mapping is defined by assigning the integer 1 to the unit element of the field. For non-prime fields or forder q=pn, each a∈GF(q) is represented – modulo the ideal generated by the Conway polynomial of degree n – by a unique polynomial fa(x)∈GF(p)[x] with deg(fa)<n. Using the standard embedding of GF(p) into ℤ we can consider fa as a polynomial over ℤ. Then, the number assigned to a is fa(p).
The mapping between GF(q) and {0,1,...,q} is provided by two functions, FfFromInt() and FfToInt(). Since the actual numeric representation of field elements depends on the kernel, you cannot convert a FEL to an integer simply by type casting.
Embedding of subfields
In the MeatAxe there is a `standard' generator for each finite field. The generator for the field currently in use is available in the FfGen variable. Thus, if a and a' are the MeatAxe generators of GF(q) and GF(q'), respectively, and q'=qn, there is a standard embedding of GF(q) into GF(q') defined by $a↪a'n. However, field elements which are identified under this embedding are usually not represented by the same number. For this reason there are two functions, FfEmbed() and FfRestrict(), which provide the embedding of subfields into the current field. Note that the MeatAxe is not well suited for calculations involving different fields at the same time because the arithmetic uses lookup tables which are specific to each field
Here is a short example. The following code converts a vector over GF(3) to GF(27). The MeatAxe cannot handle two fields at the same time, so it is necessary to unpack the row over GF(3), change to GF(27) and pack the embedded elements into a new row.
Modules | |
| File I/O | |
| Binary data files contain a sequence of objects. | |
Macros | |
| #define | FF_ZERO ((FEL)0) |
| The zero field element. | |
| #define | FF_ONE ((FEL)1) |
| The unit element. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef unsigned char | FEL |
| A finite field element. | |
| typedef FEL * | PTR |
| A pointer to a row vector. | |
Functions | |
| int | FfSetField (int field) |
| Set the field order. More... | |
| int | FfSetNoc (int noc) |
| Set the row length. More... | |
| size_t | FfRowSize (int noc) |
| Calculate row size. More... | |
| size_t | FfTrueRowSize (int noc) |
| Number of used bytes in a row. More... | |
| FEL | FfEmbed (FEL a, int subfield) |
| Embed a subfield. More... | |
| FEL | FfRestrict (FEL a, int subfield) |
| Restrict to a subfield. More... | |
| FEL | FfAdd (FEL a, FEL b) |
| Long ints per row. More... | |
| FEL | FfSub (FEL a, FEL b) |
| Finite field subtraction. More... | |
| FEL | FfMul (FEL a, FEL b) |
| Finite field multiplication. More... | |
| FEL | FfDiv (FEL a, FEL b) |
| Finite field division. More... | |
| FEL | FfNeg (FEL a) |
| Finite field negative. More... | |
| FEL | FfInv (FEL a) |
| Finite field inversion. More... | |
| void | FfAddMulRow (PTR dest, PTR src, FEL f) |
| Add a multiple of a row. More... | |
| void | FfAddMulRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, FEL f, int first, int len) |
| Add a multiple of a part of a row. More... | |
| PTR | FfAddRow (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Add two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfAddRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Add a part of two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRow (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Subtract two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Subtract a part of two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRowPartialReverse (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Subtract a part of two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfAlloc (int nor) |
| Allocate memory and initialize This function allocates a block of memory for a vector (if nrows is 1) or a matrix. More... | |
| int | FfCmpRows (PTR p1, PTR p2) |
| Compare two Rows. More... | |
| void | FfCleanRow (PTR row, PTR matrix, int nor, const int *piv) |
| Clean Row. More... | |
| int | FfCleanRow2 (PTR row, PTR mat, int nor, const int *piv, PTR row2) |
| Clean Row and Record Operations. More... | |
| int | FfCleanRowAndRepeat (PTR row, PTR mat, int nor, const int *piv, PTR row2, PTR mat2) |
| Clean Row and Repeat Operations. More... | |
| void | FfCopyRow (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Copy a row. More... | |
| FEL | FfExtract (PTR row, int col) |
| !function FfExtract "Extract a mark from a row" More... | |
| void | FfExtractColumn (PTR mat, int nor, int col, PTR result) |
| !section kernel.ff.row Extract one column of a matrix. More... | |
| int | FfFindPivot (PTR row, FEL *mark) |
| Find pivot column. More... | |
| void | FfFree (PTR x) |
| Free memory. More... | |
| FEL | FfFromInt (int l) |
| Convert integer to field element. More... | |
| PTR | FfGetPtr (PTR base, int row) |
| Get row pointer. More... | |
| void | FfInsert (PTR row, int col, FEL mark) |
| This function inserts the field element mark at position col into row. More... | |
| void | FfMulRow (PTR row, FEL mark) |
| Multiply a row by a coefficient. More... | |
| FILE * | FfReadHeader (const char *name, int *fld, int *nor, int *noc) |
| Open File and Read Header. More... | |
| int | FfReadRows (FILE *f, PTR buf, int n) |
| Read Rows This function reads 1 or more rows from a file. More... | |
| FEL | FfScalarProduct (PTR a, PTR b) |
| Scalar Product of Two Vectors. More... | |
| int | FfSeekRow (FILE *f, int pos) |
| Move to a Row. More... | |
| int | FfStepPtr (PTR *x) |
| Advance to next row. More... | |
| void | FfSwapRows (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Exchange two rows This function exchanges the contents of two rows. More... | |
| const char * | FfToGap (FEL f) |
| Convert to GAP format. More... | |
| int | FfToInt (FEL f) |
| Convert field element to integer. More... | |
| FILE * | FfWriteHeader (const char *name, int fld, int nor, int noc) |
| Open File and Write Header. More... | |
| int | FfWriteRows (FILE *f, PTR buf, int n) |
| Write rows This function writes 1 or more rows to a file. More... | |
Variables | |
| size_t | FfCurrentRowSize = (size_t) -1 |
| Row size. More... | |
| int | FfCurrentRowSizeIo = -1 |
| I/O row size. More... | |
| int | FfOrder |
| Current field order. More... | |
| int | FfChar |
| Current characteristic. More... | |
| FEL | FfGen |
| Generator. More... | |
| int | FfNoc |
| Current number of columns for row ops. More... | |
| size_t | FfCurrentRowSize |
| Row size. More... | |
| int | FfCurrentRowSizeIo |
| I/O row size. More... | |
| int | LPR |
| Number of marks per byte (depends on field order) | |
| FEL | mtx_tmult [256][256] |
| table for field element multiplication | |
| FEL | mtx_tadd [256][256] |
| table for field element addition | |
| FEL | mtx_taddinv [256] |
| table for field element negation | |
| FEL | mtx_tmultinv [256] |
| table for field element inversion | |
| FEL | mtx_tffirst [256][2] |
| table for value and index of the first non-zero mark in byte | |
| FEL | mtx_textract [8][256] |
| table for extraction of a mark from a byte | |
| FEL | mtx_tinsert [8][256] |
| table for insertion of a mark into a byte | |
| int | FfOrder = -1 |
| Field order. More... | |
| FEL | FfGen = 0 |
| Field generator. More... | |
| int | FfNoc = 0 |
| Current row size. More... | |
Function Documentation
Long ints per row.
Finite field addition.
This function returns the sum of two field elements. Before calling FfAdd(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The arguments are not checked. If either argument is not in the allowed range the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfAdd() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that both arguments are evaluated exactly once.
Add a multiple of a row.
This function adds a scalar multiple of src to dest.
- Parameters
-
dest row to add to. src row to be multiplied with f and added to dest. f field element.
Add a multiple of a part of a row.
This function adds a multiple of src to dest. This works like FfAddRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns.
- Parameters
-
dest row to add to. src row to be multiplied with f and added to dest. f field element. first number of bytes to skip. len number of bytes to process.
Add two rows.
This function adds src to dest. Field order and row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to add to. src The row to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Add a part of two rows.
This works like FfAddRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns. Note that the working range is not specified as column indexes but in units of long integers!
- Parameters
-
dest The row to add to. src The row to add. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
| PTR FfAlloc | ( | int | nrows | ) |
Allocate memory and initialize This function allocates a block of memory for a vector (if nrows is 1) or a matrix.
Memory is initialized to zero. Field order and row size must have been set with FfSetField() and FfSetNoc(), respectively. nrows may be zero zero, i which case the functin returns a memory block of size zero which must be freed using FfFree().
- Parameters
-
nrows Number of rows.
- Returns
- Pointer to the memory block or NULL on error.
Clean Row.
This function performs a Gaussian elimination, i.e., it adds suitable multiples of the rows of matrix to row such that all pivot positions are zero. piv is the pivot table for matrix. As usual, all indexes are 0-based, i.e., piv[0] is the pivot column of the first row, and for a unit matrix we have piv[0]==0. The field and row size must have been set before calling this function.
- Parameters
-
row The row to be cleaned. matrix Pointer to the matrix. nor Number of rows of the matrix. piv The pivot table.
Clean Row and Record Operations.
This function works like FfCleanRow(), but it stores a record of the operations performed in row2. row2 must be a row of at least nor entries. On return, row2 contains the coefficients by which the rows of mat were multiplied and then subtracted from row. Before calling FfCleanRow2(), the caller must initialize row2 to zero. Otherwise the results are undefined.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to row to be cleaned. mat Matrix to clean with. nor Number of rows. piv Pivot table for matrix. row2 Pointer to row where the operations are recorded.
- Returns
- 0, or 1 on error.
Clean Row and Repeat Operations.
This function works like FfCleanRow(), but repeats all operations on a second row/matrix.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to row to be cleaned. mat Matrix to clean with. nor Number of rows. piv Pivot table for mat. row2 Pointer to the second row to be cleaned. mat2 Matrix to the second matrix.
- Returns
- 0, or 1 on error.
Compare two Rows.
This function compares two row vectors. As with all row operations, the row length must have been set before with FfSetNoc(). The return value is negative if the first row is "less" than the second row, and it is positive if the first row is "greater" than the second row. However, the ordering defined by FfCmpRows() depends on the internal representation of finite field elements and can differ between dirrerent kernels or between different hardware architectures.
- Parameters
-
p1 Pointer to the first matrix. p2 Pointer to the second matrix.
- Returns
- The function returns 0 if the two rows are identical. Otherwise the return value is different from 0.
Copy a row.
This function copies the contents of one row to another row. As with all row operations, the row length must have been set before with |FfSetNoc()|.
- Parameters
-
dest Pointer to the destination. src Pointer to the source.
Finite field division.
This function returns the quotient of two field elements. Before calling FfDiv(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The arguments are not checked. If either argument is not in the allowed range or if the denominator is zero, the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfDiv() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that both arguments are evaluated exactly once.
Embed a subfield.
- Parameters
-
a Element of the subfield field. subfield Subfield order. Must be a divisor of the current field order.
- Returns
- a, embedded into the current field, or 255 on error.
!function FfExtract "Extract a mark from a row"
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. col Index of mark to extract (0-based).
- Returns
- |col|-th entry of |row|. !description This function returns the entry at position |col| of a row. Note that column indexes start with 0, i.e., |FfExtract(row,0)| returns the first entry of a row. Like |FfInsert()|, this function does not depend on the current row size. Reading beyond the end of a row will probably not produce an error, but the result is undefined.
- See also
- FfInsert()
!section kernel.ff.row Extract one column of a matrix.
- Parameters
-
mat Pointer to the matrix. nor Number of rows in matrix. col Column to extract (starting with 1). result Pointer to buffer for the extracted column. !description This function extracts one column out of a matrix and stores it as a row vector in |result|. The number of columns of the matrix must have been set with |FfSetNoc()|. |nor| is the number of rows in the matrix. The result is a row with |nor| entries, i.e., the length of |result| must be at least |nor|. |mat| and |result| must not overlap, or the result is undefined.
Find pivot column.
This function scans the vector row and finds the first non-zero mark. The mark is stored into *mark and its position (counting from 0) is returned. If the whole vector is zero, FfFindPivot() returns -1 and leaves *mark unchanged.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. mark Buffer for pivot element.
- Returns
- Index of the first non-zero entry in row or -1 if all entries are zero.
| void FfFree | ( | PTR | x | ) |
Free memory.
This function frees a block of memory that has been allocated with FfAlloc() before. If the argument is 0, FfFree() does nothing.
- Parameters
-
x Pointer to memory.
| FEL FfFromInt | ( | int | l | ) |
Convert integer to field element.
This function converts an integer to a field element using the same mapping as explained under FfToInt(). Both functions are inverse in the sense that the expression f == FfFromInt(FfToInt(f)) is always true for valid field elements. FfFromInt() should be used whenever field elements are to be read with scanf().
Get row pointer.
This function returns a pointer to the |nor|-th row of a matrix, assuming the current row size. |base| must be a pointer to the beginning of a row, but this need not be the first row of the matrix. For example, the following code steps through the odd rows of a matrix:
Note: The function does not check if the resulting pointer is still inside the matrix.
- See also
- FfStepPtr()
- Parameters
-
base Pointer to the first row of the matrix. row Row index.
This function inserts the field element mark at position col into row.
Column indexes start with 0. Before this function can be used, the field must be selected with FfSetField(). FfInsert() does not need the row size beeing set correctly. For example, if you are working with rows of different size, you do not have to call FfSetNoc() prior to each FfInsert(). On the other hand, there is no protection against writing beyond the end of a row.
If the MeatAxe is compiled with the DEBUG option FfInsert() checks that mark is a valid field element and col is not negative. If also the PARANOID option was in effect during compilation, FfInsert() also checks if col is less than or equal to the current row size.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. col Insert position (0-based). mark Value to insert.
| FfInv | ( | FEL | a | ) |
Finite field inversion.
This function returns the multiplicative inverse a field element. Before calling FfInv(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The argument is not checked. If you pass an invalid value or zero, the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfInv() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that the argument is evaluated exactly once.
Finite field multiplication.
This function returns the product of two field elements. Before calling FfMul(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The arguments are not checked. If either argument is not in the allowed range the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfMul() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that both arguments are evaluated exactly once.
Multiply a row by a coefficient.
This function multiplies each element of row by mark. The row size and field order must have been set before. Multiplying a row with zero (FF_ZERO) initializes all elements to zero and is permitted even if row points into uninitialized memory.
| FfNeg | ( | FEL | a | ) |
Finite field negative.
This function returns the additive inverse a field element. Before calling FfInv(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The argument is not checked. If you pass an invalid value, the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfNeg() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that the argument is evaluated exactly once.
| FILE* FfReadHeader | ( | const char * | name, |
| int * | field, | ||
| int * | nor, | ||
| int * | noc | ||
| ) |
Open File and Read Header.
This function opens a data file for input and reads the file header (3 integers). The exact meaning of the header values depends on the file type. For a matrix they are field order, number of rows and number of columns.
- Parameters
-
name File name. field Pointer to buffer for first header entry (usually the field order). nor Pointer to buffer for second header entry (usually the number of rows). noc Pointer to buffer for third header entry (usually the number of columns).
- Returns
- Pointer to open file, or 0 on error.
| int FfReadRows | ( | FILE * | f, |
| PTR | buf, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
Read Rows This function reads 1 or more rows from a file.
The row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
f Pointer to File. buf Pointer to data buffer. n Number of rows to read.
- Returns
- Number of rows that were actually read, or -1 on error.
Restrict to a subfield.
This function restricts a field element from the current field to a subfield. The return value represents the same element as a but with respect to the subfield. In general, the element has a different integer representation in the subfield. Consequently, you cannot use the return value for field arithmetic until you change to the subfield with Of course, the argument must be an element of the subfield. Otherwise the result is undefined. FfSetField(subfield).
- Parameters
-
a Element of the current field. subfield Subfield order. Must be a divisor of the current field order. Return 255 on error.
| size_t FfRowSize | ( | int | noc | ) |
Calculate row size.
Returns the number of bytes occupied in memory by a row of noc Elements. The row size is always a multiple of sizeof(long). Depending on the number of columns there may be unused padding bytes at the end of the row.
Scalar Product of Two Vectors.
Given two vectors 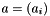 and
and 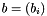 , this function calculates the scalar product
, this function calculates the scalar product 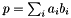 .
.
- Parameters
-
a The first vector. b The second vector.
- Returns
- Scalar product of the two vectors.
| int FfSeekRow | ( | FILE * | f, |
| int | pos | ||
| ) |
Move to a Row.
This function sets the read/write pointer of file f to position pos. I.e., the next FfReadRows() or FfWriteRows() will start at the specified row. Note that row numbers start with 0. If pos is different from 0, the row size must have been set before with FfSetNoc().
You should always use FfSeekRow() rather than fseek() because FfSeekRow() knows about MeatAxe file headers and adjusts the file pointer appropriately.
- Parameters
-
f Pointer to File. pos Row number (0-based).
- Returns
- 0 on success, -1 on error.
| int FfSetField | ( | int | field | ) |
Set the field order.
This function sets the current field to GF(field) and initializes the field arithmetic. Most kernel functions require that a field has been selected before they are used.
- Parameters
-
field Field order.
- Returns
- 0 on success, -1 otherwise.
| int FfSetNoc | ( | int | noc | ) |
Set the row length.
This function sets the current row size, which is used for low-level row operations such as FfAddRow().
- Parameters
-
noc Number of columns.
- Returns
- 0 on success, -1 otherwise.
| int FfStepPtr | ( | PTR * | x | ) |
Advance to next row.
This function increments a pointer by 1 row. The row size must have been set before with FfSetNoc(). FfStepPtr(&x) is equivalent to x = FfGetPtr(x,1). It is typically used to step through the rows of a matrix. Here is an example with a 100 by 40 matrix:
- See also
- FfGetPtr()
- Parameters
-
x Pointer to the row pointer.
- Returns
- Always 0.
Finite field subtraction.
This function returns the difference of two field elements. Before calling FfSub(), the field must have been selected with FfSetField(). The arguments are not checked. If either argument is not in the allowed range the result is undefined and the program may crash. FfSub() may be implemented as a macro. In this case, it is guaranteed that both arguments are evaluated exactly once.
Subtract two rows.
This function subtracts src from dest. Field order and row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract from. src The row to subtract.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Subtract a part of two rows.
This works like FfSubRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns. Note that the working range is not specified as column indexes but in units of long integers!
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract from. src The row to subtract. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Subtract a part of two rows.
The difference to FfSubRowPartial is that dest is replaced by src-dest, not by dest-src.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract. src The row to subtract from. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Exchange two rows This function exchanges the contents of two rows.
As with all row operations, the row length must have been set before with |FfSetNoc()|.
- Parameters
-
dest Pointer to the first row src Pointer to the second row
| const char* FfToGap | ( | FEL | f | ) |
Convert to GAP format.
This function takes a field element and returns the GAP representation of this element. The return value is a pointer to a static buffer which is overwritten on each call.
- Parameters
-
f Field element.
- Returns
- Pointer to the GAP representtion of f.
| int FfToInt | ( | FEL | f | ) |
Convert field element to integer.
This function converts a field element to an integer, using a "canonical" representation of field elements as integers which may be different from the internal representation. In particular, the prime field is mapped on {0,...p-1} with 0 representing the zero element and 1 the unit element. FfToInt() should be used whenever field elements are to be written with printf().
| size_t FfTrueRowSize | ( | int | noc | ) |
Number of used bytes in a row.
This function returns the number of bytes that are actually used by a row of noc Elements, i.e., without counting the padding bytes. This number is less than or equal to FfRowSize(noc).
| FILE* FfWriteHeader | ( | const char * | name, |
| int | field, | ||
| int | nor, | ||
| int | noc | ||
| ) |
Open File and Write Header.
This function opens a data file for input and writes the the file header. If the file does not exist, a new file is created. If the file exists it is overwritten.
- Parameters
-
name File name. field First header entry (usually the field order). nor Second header entry (usually the number of rows). noc Third header entry (usually the number of columns).
- Returns
- Pointer to open file, or |NULL| on error.
| int FfWriteRows | ( | FILE * | f, |
| PTR | buf, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
Write rows This function writes 1 or more rows to a file.
The row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
f Pointer to File. buf Pointer to data buffer. n Number of rows to write.
- Returns
- The number of rows that were successully written. A return value different from |n| indicates an error.
Variable Documentation
| int FfChar |
Current characteristic.
Current characteristic.
Characteristic of the current field. Like FfOrder, this variable may be used anywhere, but it must not be modified directly.
| size_t FfCurrentRowSize |
Row size.
This variable contains the size of a single row in memory. Its value is always equal to FfRowSize(FfNoc). The row size os always a multiple of sizeof(long).
| size_t FfCurrentRowSize = (size_t) -1 |
Row size.
This variable contains the size of a single row in memory. Its value is always equal to FfRowSize(FfNoc). The row size os always a multiple of sizeof(long).
| int FfCurrentRowSizeIo |
I/O row size.
This variable contains the number of bytes occupied by a row when stored in a data file. Its value is always equal to FfTrueRowSize(FfNoc). Since there is no padding in data files, FfCurrentRowSizeIo is usually smaller than FfCurrentRowSize.
| int FfCurrentRowSizeIo = -1 |
I/O row size.
This variable contains the number of bytes occupied by a row when stored in a data file. Its value is always equal to FfTrueRowSize(FfNoc). Since there is no padding in data files, FfCurrentRowSizeIo is usually smaller than FfCurrentRowSize.
| FEL FfGen = 0 |
Field generator.
Generator.
This variable contains a genrator for the multiplicative group of the current field.
| FEL FfGen |
Generator.
Generator.
This variable contains a genrator for the multiplicative group of the current field.
| int FfNoc = 0 |
Current row size.
Current number of columns for row ops.
Used by all low-level row operations. FfNoc is updated automatically when the row size is changed with FfSetNoc().
| int FfNoc |
Current number of columns for row ops.
Current number of columns for row ops.
Used by all low-level row operations. FfNoc is updated automatically when the row size is changed with FfSetNoc().
| int FfOrder = -1 |
Field order.
Current field order.
FfOrder may be used in expressiond but must never modified directly. To change the current field, use FfSetField().
| int FfOrder |
Current field order.
Current field order.
FfOrder may be used in expressiond but must never modified directly. To change the current field, use FfSetField().