Detailed Description
All row operations at kernel level use a global row size which can be set with FfSetNoc().
The current row size is available in the global variable FfNoc.
A (row) vector is stored in memory as an array of bytes. The actual size of a row depends on the number of marks in the row and on the field order, because several field elements may be packed into one byte. However, the size is always a multiple of sizeof(long). Thus, there may be unused bytes at the end of a row. The contents of these extra bytes (and even the contents of unused bits in partially used bytes) is not defined. For this reason, memory must be initialized before it is used, or else some functions as FfCmpRows() may fail.
Packing of field elements is used for field orders less than 17. Let q be the field order and m the largest natural number with qm≤256. Then, m elements k0,...kn-1 are packed into one byte as k0+k1q+k2q2+... Packing of field elements is used exclusively for rows (vectors), not for polynomials or other data types.
Because of packing you cannot access the marks of a row with the usual bracket notation. Instead, the MeatAxe library provides functions which store and extract marks.
Packed rows must be initialized before they are used. FfInsert() (and many other row operations) will produce strange results if used with uninitialized rows. Memory is initialized automatically in the following cases: allocation with FfAlloc(), copying a row with FfCopyRow(), reading a row from a file. A row can be initialized manually by multiplication with zero: FfMulRow(ptr,FF_ZERO). The latter works even if no field has been selected.
A matrix is stored as a sequence of rows with no extra space between them. The rows and columns of a matrix are numbered 0,1,2,...n-1. Column vectors may be stored as matrices with one column but each mark of the vector will occupy 4 Bytes.
Functions | |
| PTR | FfAddRow (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Add two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfAddRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Add a part of two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRow (PTR dest, PTR src) |
| Subtract two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Subtract a part of two rows. More... | |
| PTR | FfSubRowPartialReverse (PTR dest, PTR src, int first, int len) |
| Subtract a part of two rows. More... | |
| void | FfAddMulRowPartial (PTR dest, PTR src, FEL f, int first, int len) |
| Add a multiple of a part of a row. More... | |
| void | FfMulRow (PTR row, FEL mark) |
| Multiply a row by a coefficient. More... | |
| void | FfAddMulRow (PTR dest, PTR src, FEL f) |
| Add a multiple of a row. More... | |
| FEL | FfFromInt (int l) |
| Convert integer to field element. More... | |
| int | FfToInt (FEL f) |
| Convert field element to integer. More... | |
| void | FfMapRow (PTR row, PTR matrix, int nor, PTR result) |
| Multiply a vector by a matrix. More... | |
| FEL | FfScalarProduct (PTR a, PTR b) |
| Scalar Product of Two Vectors. More... | |
| void | FfExtractColumn (PTR mat, int nor, int col, PTR result) |
| !section kernel.ff.row Extract one column of a matrix. More... | |
| void | FfInsert (PTR row, int col, FEL mark) |
| This function inserts the field element mark at position col into row. More... | |
| FEL | FfExtract (PTR row, int col) |
| !function FfExtract "Extract a mark from a row" More... | |
| int | FfFindPivot (PTR row, FEL *mark) |
| Find pivot column. More... | |
Function Documentation
Add a multiple of a row.
This function adds a scalar multiple of src to dest.
- Parameters
-
dest row to add to. src row to be multiplied with f and added to dest. f field element.
Add a multiple of a part of a row.
This function adds a multiple of src to dest. This works like FfAddRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns.
- Parameters
-
dest row to add to. src row to be multiplied with f and added to dest. f field element. first number of bytes to skip. len number of bytes to process.
Add two rows.
This function adds src to dest. Field order and row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to add to. src The row to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Add a part of two rows.
This works like FfAddRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns. Note that the working range is not specified as column indexes but in units of long integers!
- Parameters
-
dest The row to add to. src The row to add. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
!function FfExtract "Extract a mark from a row"
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. col Index of mark to extract (0-based).
- Returns
- |col|-th entry of |row|. !description This function returns the entry at position |col| of a row. Note that column indexes start with 0, i.e., |FfExtract(row,0)| returns the first entry of a row. Like |FfInsert()|, this function does not depend on the current row size. Reading beyond the end of a row will probably not produce an error, but the result is undefined.
- See also
- FfInsert()
!section kernel.ff.row Extract one column of a matrix.
- Parameters
-
mat Pointer to the matrix. nor Number of rows in matrix. col Column to extract (starting with 1). result Pointer to buffer for the extracted column. !description This function extracts one column out of a matrix and stores it as a row vector in |result|. The number of columns of the matrix must have been set with |FfSetNoc()|. |nor| is the number of rows in the matrix. The result is a row with |nor| entries, i.e., the length of |result| must be at least |nor|. |mat| and |result| must not overlap, or the result is undefined.
Find pivot column.
This function scans the vector row and finds the first non-zero mark. The mark is stored into *mark and its position (counting from 0) is returned. If the whole vector is zero, FfFindPivot() returns -1 and leaves *mark unchanged.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. mark Buffer for pivot element.
- Returns
- Index of the first non-zero entry in row or -1 if all entries are zero.
| FEL FfFromInt | ( | int | l | ) |
Convert integer to field element.
This function converts an integer to a field element using the same mapping as explained under FfToInt(). Both functions are inverse in the sense that the expression f == FfFromInt(FfToInt(f)) is always true for valid field elements. FfFromInt() should be used whenever field elements are to be read with scanf().
This function inserts the field element mark at position col into row.
Column indexes start with 0. Before this function can be used, the field must be selected with FfSetField(). FfInsert() does not need the row size beeing set correctly. For example, if you are working with rows of different size, you do not have to call FfSetNoc() prior to each FfInsert(). On the other hand, there is no protection against writing beyond the end of a row.
If the MeatAxe is compiled with the DEBUG option FfInsert() checks that mark is a valid field element and col is not negative. If also the PARANOID option was in effect during compilation, FfInsert() also checks if col is less than or equal to the current row size.
- Parameters
-
row Pointer to the row. col Insert position (0-based). mark Value to insert.
Multiply a vector by a matrix.
This function multiplies the vector row from the right by the matrix mat and stores the result into result. The number of columns in both mat and result is determined by the current row size. (
- See also
- FfNoc()).
- Attention
- result and row must not overlap. Otherwise the result is undefined.
- Parameters
-
row The source vector (FfNoc columns). matrix The matrix (nor by FfNoc). nor number of rows in the matrix. [out] result The resulting vector (nor columns).
Multiply a row by a coefficient.
This function multiplies each element of row by mark. The row size and field order must have been set before. Multiplying a row with zero (FF_ZERO) initializes all elements to zero and is permitted even if row points into uninitialized memory.
Scalar Product of Two Vectors.
Given two vectors 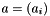 and
and 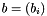 , this function calculates the scalar product
, this function calculates the scalar product 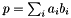 .
.
- Parameters
-
a The first vector. b The second vector.
- Returns
- Scalar product of the two vectors.
Subtract two rows.
This function subtracts src from dest. Field order and row size must have been set before.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract from. src The row to subtract.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Subtract a part of two rows.
This works like FfSubRow(), but the operation is performed only on a given range of columns. Note that the working range is not specified as column indexes but in units of long integers!
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract from. src The row to subtract. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
Subtract a part of two rows.
The difference to FfSubRowPartial is that dest is replaced by src-dest, not by dest-src.
- Parameters
-
dest The row to subtract. src The row to subtract from. first Number of long integers to skip. len Number of long integers to add.
- Returns
- Always returns dest.
| int FfToInt | ( | FEL | f | ) |
Convert field element to integer.
This function converts a field element to an integer, using a "canonical" representation of field elements as integers which may be different from the internal representation. In particular, the prime field is mapped on {0,...p-1} with 0 representing the zero element and 1 the unit element. FfToInt() should be used whenever field elements are to be written with printf().